

Living Better Together
http://csatc.org Compassionate Sciences Alternative Treatment Center - New Jersey Medical Marijuana Dispensary Compassionate Sciences Alternative Treatment Center is a New Jersey State-recognized designated dispensary of medicinal marijuana.


Living Better Together
Cannabinoids bind with special receptors on cell membranes.
When bound to receptors, cannabinoids mitigate pain, suppress nausea, decrease ocular pressure and enhance appetite.
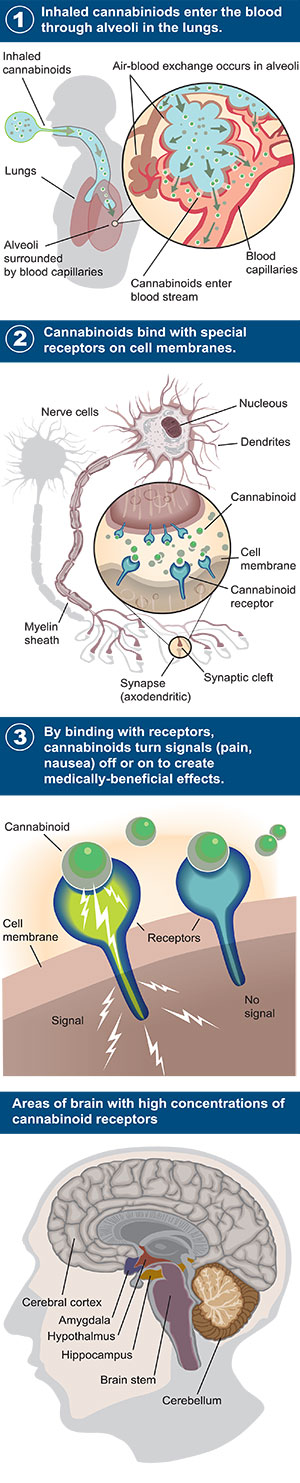
Cannabinoids are delivered to the bloodstream through the lungs (when inhaled), the digestive system (when consumed) or the skin (when applied topically). Once in the bloodstream, they are available to the brain and central nervous system.
Inhalation is the fastest method, with peak blood levels achieved within 20 minutes. Oral ingestion is slower because the cannabinoids go through the gastrointestinal tract before entering the bloodstream – which takes more time. The bioavailabilityThe degree to which a drug or other substance becomes available to the target tissue after administration. of cannabinoids in the body is an important area of ongoing research with implications for the medicinal use of Cannabis. Please see an example of cannabinoid bioavailability below.
Typical plasma levels of THC after smoking Cannabis are 70-160 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). Because THC is lipid-soluble, it rapidly leaves the bloodstream and goes into the fatty tissues of the body. When Cannabis is smoked or inhaled, only about 10-25% of THC is absorbed into the bloodstream from the lungs and about 1% of that reaches the brain rapidly. This is important because brain cells possess unique binding sites for cannabinoids called cannabinoid receptors. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they trigger the pharmacological effects such as pain mitigation, nausea suppression and appetite stimulation. After the patient stops ingesting Cannabis, plasma levels of THC typically decrease to less than 20 ng/ml within 30-45 minutes. Pharmacological activity peaks at about 20 minutes after inhalation and is gone within 3 hours. When ingested orally, the pharmacological effects of THC are delayed by 30-90 minutes, peak after 2-3 hours and last for 4-12 hours. Bioavailability by ingestion is affected by liver metabolism and varies greatly (4-12%), making oral treatments difficult to manage.
In 1988, a major breakthrough in our understanding of Cannabis took place when American scientist Dr. Allyn HowlettPhD., pharmacology and toxicology, at Wake Forest School of Medicine. discovered cannabinoid receptors in the human brain. Basically, these receptors are protein molecules embedded in cellular surfaces that receive chemical signals from other cells. These signals result in a range of effects from pain to nausea and euphoria to depression. They can stimulate or suppress appetite or growth, while also impacting mood and perception. Cannabinoid receptors have also been discovered in mammals, birds, fish and reptiles.
There are two major types of cannabinoid receptors in our bodies, CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptors are found in the central nervous system, on brain cells and in the peripheral nervous systemThe part of the vertebrate nervous system constituting the nerves outside the central nervous system and including the cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The CB2 receptors are generally found on immune cellsAny of several types of blood cells that help defend the body from infection. Humans have many thousands of receptors that we still have not identified or fully understood. A common characteristic is that receptors bind with naturally-occurring substances such as hormones (e.g., estrogen, testosterone) and growth factors (e.g., insulin) as well as with exogenousDerived or developed from outside the body; originating externally. substances introduced into the body to mimic the effect of endogenousOriginating or produced within an organism, tissue, or cell. substances.
Substances that activate receptors after binding with them are called agonistsA drug or other chemical that can combine with a receptor on a cell to produce a physiologic reaction typical of a naturally occurring substance. Those that suppress the ability of the receptor to activate are called antagonistsA chemical substance that interferes with the physiological action of another, especially by combining with and blocking its nerve receptor. Generally, agonists have the effect of turning receptors on while antagonists turn them off. As a result, the signal running along the neural pathwayConnects one part of the nervous system with another. where the receptor is located is either enhanced or suppressed. Cannabinoids have been shown to stimulate the CB1 and CB2 receptors in a number of ways, serving as agonists, antagonists or as both.
Having discovered cannabinoid receptors, scientists began to search for the naturally-occurring ligandAn ion, a molecule, or a molecular group that binds to another chemical entity to form a larger complex. that binds with the receptors to achieve a biologic purpose. Their research uncovered two endocannabinoidsCannabinoids that occur naturally in the human body. in the human body: anandamide N-arachidonoyl ethanolamide, or AEA. and 2–AG.2-arachidonoylglycerol. Both are agonists that influence pain, appetite, motor learning and synaptic plasticity.The strength or weakness of signals between cells.
In the bloodstream, exogenous cannabinoids act like endocannabinoids, binding with receptors to mitigate pain, suppress nausea, decrease ocularOf or relating to the eye. pressure and enhance appetite. Thus, as far as we know, Cannabis does not cure anything. Instead, the plant’s active ingredients can deliver important palliative effects. Note: the stimulation of the CB receptors by exogenous cannabinoids is complex, as not all cannabinoids interact with the receptors in the same way. Because of this, scientists are still trying to unravel the details of the system and its implications for medicine.
Currently, medical Cannabis is used to treat the symptoms – and the side-effects of treatments for – cancer, Crohn’s DiseaseAn inflammatory disease of the intestines also known as regional enteritis., epilepsy and other seizure disorders, glaucoma, multiple sclerosis, neuropathic pain, rheumatoid arthritis and cachexia.A profound wasting and physical debility with severe emaciation, weight and hair loss, dry and flabby skin, disappearance of subcutaneous fat, atrophy of muscles and viscera and low serum protein level. Medical studies are exploring the use of Cannabis to suppress muscle spasms and spasticity, relieve chronic pain, manage glaucoma and bronchial asthma.